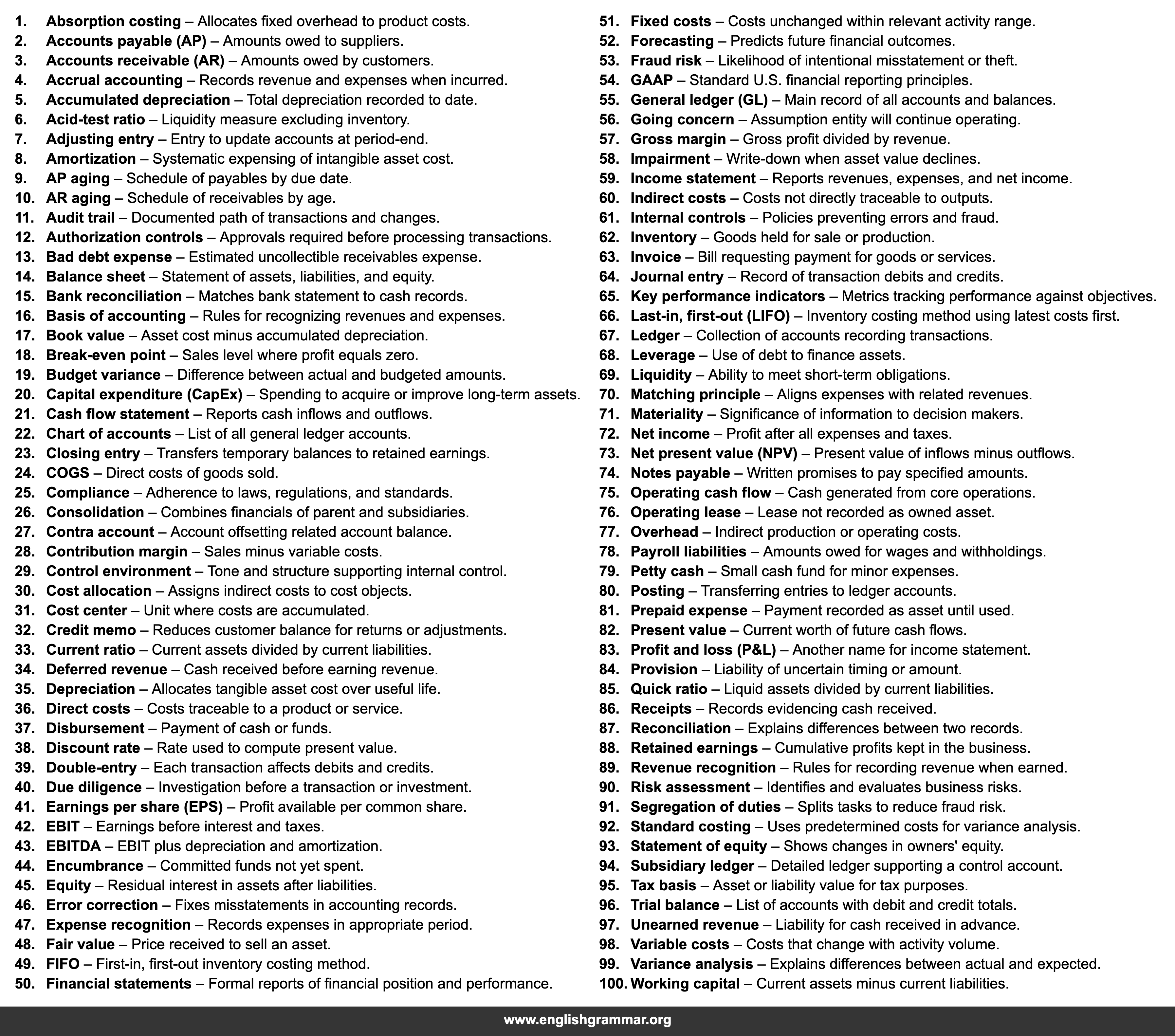
| No. | Term | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Absorption costing | Allocates fixed overhead to product costs. |
| 2. | Accounts payable (AP) | Amounts owed to suppliers. |
| 3. | Accounts receivable (AR) | Amounts owed by customers. |
| 4. | Accrual accounting | Records revenue and expenses when incurred. |
| 5. | Accumulated depreciation | Total depreciation recorded to date. |
| 6. | Acid-test ratio | Liquidity measure excluding inventory. |
| 7. | Adjusting entry | Entry to update accounts at period-end. |
| 8. | Amortization | Systematic expensing of intangible asset cost. |
| 9. | AP aging | Schedule of payables by due date. |
| 10. | AR aging | Schedule of receivables by age. |
| 11. | Audit trail | Documented path of transactions and changes. |
| 12. | Authorization controls | Approvals required before processing transactions. |
| 13. | Bad debt expense | Estimated uncollectible receivables expense. |
| 14. | Balance sheet | Statement of assets, liabilities, and equity. |
| 15. | Bank reconciliation | Matches bank statement to cash records. |
| 16. | Basis of accounting | Rules for recognizing revenues and expenses. |
| 17. | Book value | Asset cost minus accumulated depreciation. |
| 18. | Break-even point | Sales level where profit equals zero. |
| 19. | Budget variance | Difference between actual and budgeted amounts. |
| 20. | Capital expenditure (CapEx) | Spending to acquire or improve long-term assets. |
| 21. | Cash flow statement | Reports cash inflows and outflows. |
| 22. | Chart of accounts | List of all general ledger accounts. |
| 23. | Closing entry | Transfers temporary balances to retained earnings. |
| 24. | COGS | Direct costs of goods sold. |
| 25. | Compliance | Adherence to laws, regulations, and standards. |
| 26. | Consolidation | Combines financials of parent and subsidiaries. |
| 27. | Contra account | Account offsetting related account balance. |
| 28. | Contribution margin | Sales minus variable costs. |
| 29. | Control environment | Tone and structure supporting internal control. |
| 30. | Cost allocation | Assigns indirect costs to cost objects. |
| 31. | Cost center | Unit where costs are accumulated. |
| 32. | Credit memo | Reduces customer balance for returns or adjustments. |
| 33. | Current ratio | Current assets divided by current liabilities. |
| 34. | Deferred revenue | Cash received before earning revenue. |
| 35. | Depreciation | Allocates tangible asset cost over useful life. |
| 36. | Direct costs | Costs traceable to a product or service. |
| 37. | Disbursement | Payment of cash or funds. |
| 38. | Discount rate | Rate used to compute present value. |
| 39. | Double-entry | Each transaction affects debits and credits. |
| 40. | Due diligence | Investigation before a transaction or investment. |
| 41. | Earnings per share (EPS) | Profit available per common share. |
| 42. | EBIT | Earnings before interest and taxes. |
| 43. | EBITDA | EBIT plus depreciation and amortization. |
| 44. | Encumbrance | Committed funds not yet spent. |
| 45. | Equity | Residual interest in assets after liabilities. |
| 46. | Error correction | Fixes misstatements in accounting records. |
| 47. | Expense recognition | Records expenses in appropriate period. |
| 48. | Fair value | Price received to sell an asset. |
| 49. | FIFO | First-in, first-out inventory costing method. |
| 50. | Financial statements | Formal reports of financial position and performance. |
| 51. | Fixed costs | Costs unchanged within relevant activity range. |
| 52. | Forecasting | Predicts future financial outcomes. |
| 53. | Fraud risk | Likelihood of intentional misstatement or theft. |
| 54. | GAAP | Standard U.S. financial reporting principles. |
| 55. | General ledger (GL) | Main record of all accounts and balances. |
| 56. | Going concern | Assumption entity will continue operating. |
| 57. | Gross margin | Gross profit divided by revenue. |
| 58. | Impairment | Write-down when asset value declines. |
| 59. | Income statement | Reports revenues, expenses, and net income. |
| 60. | Indirect costs | Costs not directly traceable to outputs. |
| 61. | Internal controls | Policies preventing errors and fraud. |
| 62. | Inventory | Goods held for sale or production. |
| 63. | Invoice | Bill requesting payment for goods or services. |
| 64. | Journal entry | Record of transaction debits and credits. |
| 65. | Key performance indicators | Metrics tracking performance against objectives. |
| 66. | Last-in, first-out (LIFO) | Inventory costing method using latest costs first. |
| 67. | Ledger | Collection of accounts recording transactions. |
| 68. | Leverage | Use of debt to finance assets. |
| 69. | Liquidity | Ability to meet short-term obligations. |
| 70. | Matching principle | Aligns expenses with related revenues. |
| 71. | Materiality | Significance of information to decision makers. |
| 72. | Net income | Profit after all expenses and taxes. |
| 73. | Net present value (NPV) | Present value of inflows minus outflows. |
| 74. | Notes payable | Written promises to pay specified amounts. |
| 75. | Operating cash flow | Cash generated from core operations. |
| 76. | Operating lease | Lease not recorded as owned asset. |
| 77. | Overhead | Indirect production or operating costs. |
| 78. | Payroll liabilities | Amounts owed for wages and withholdings. |
| 79. | Petty cash | Small cash fund for minor expenses. |
| 80. | Posting | Transferring entries to ledger accounts. |
| 81. | Prepaid expense | Payment recorded as asset until used. |
| 82. | Present value | Current worth of future cash flows. |
| 83. | Profit and loss (P&L) | Another name for income statement. |
| 84. | Provision | Liability of uncertain timing or amount. |
| 85. | Quick ratio | Liquid assets divided by current liabilities. |
| 86. | Receipts | Records evidencing cash received. |
| 87. | Reconciliation | Explains differences between two records. |
| 88. | Retained earnings | Cumulative profits kept in the business. |
| 89. | Revenue recognition | Rules for recording revenue when earned. |
| 90. | Risk assessment | Identifies and evaluates business risks. |
| 91. | Segregation of duties | Splits tasks to reduce fraud risk. |
| 92. | Standard costing | Uses predetermined costs for variance analysis. |
| 93. | Statement of equity | Shows changes in owners’ equity. |
| 94. | Subsidiary ledger | Detailed ledger supporting a control account. |
| 95. | Tax basis | Asset or liability value for tax purposes. |
| 96. | Trial balance | List of accounts with debit and credit totals. |
| 97. | Unearned revenue | Liability for cash received in advance. |
| 98. | Variable costs | Costs that change with activity volume. |
| 99. | Variance analysis | Explains differences between actual and expected. |
| 100. | Working capital | Current assets minus current liabilities. |