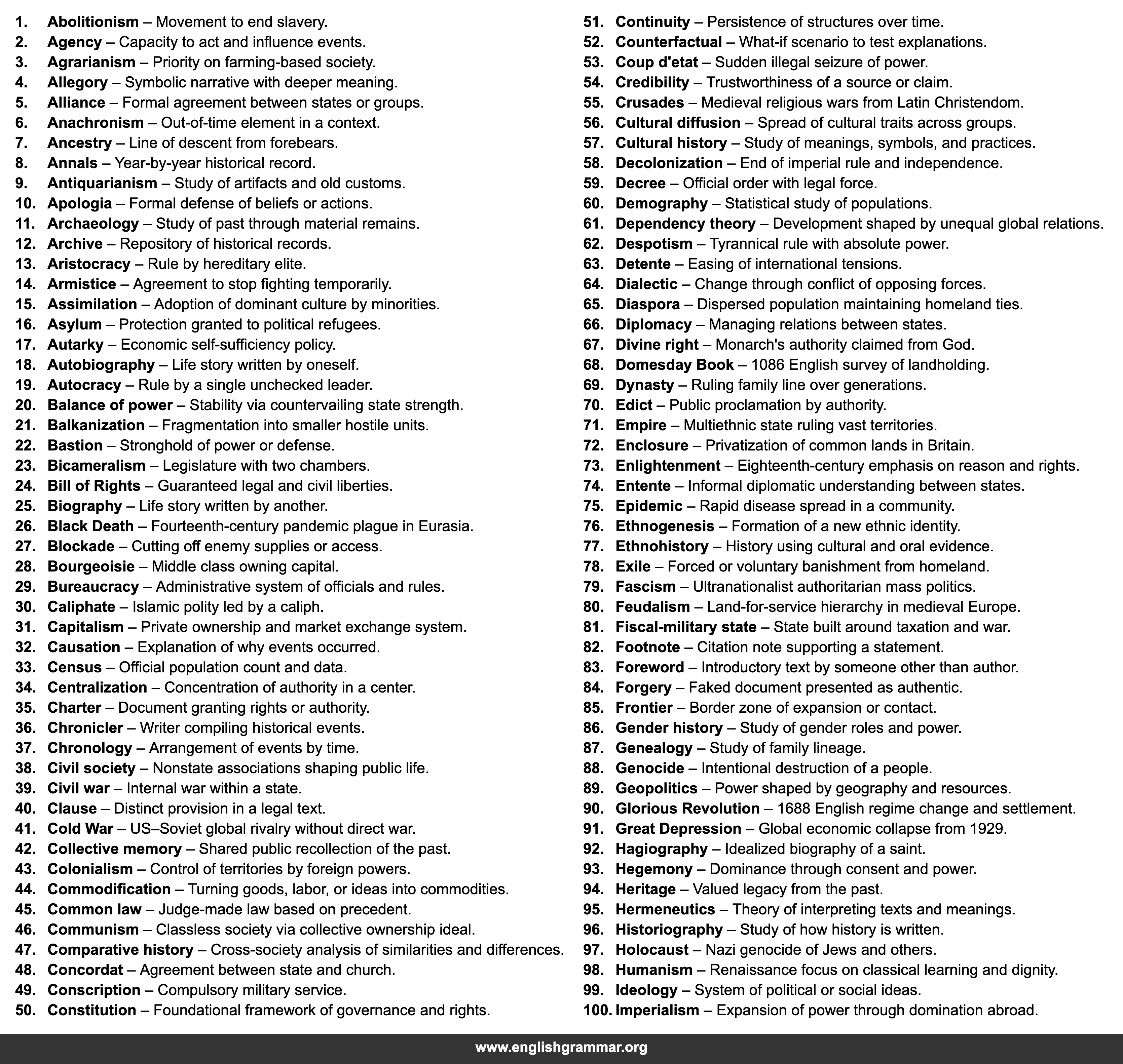
| No. | Term | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Abolitionism | Movement to end slavery. |
| 2. | Agency | Capacity to act and influence events. |
| 3. | Agrarianism | Priority on farming-based society. |
| 4. | Allegory | Symbolic narrative with deeper meaning. |
| 5. | Alliance | Formal agreement between states or groups. |
| 6. | Anachronism | Out-of-time element in a context. |
| 7. | Ancestry | Line of descent from forebears. |
| 8. | Annals | Year-by-year historical record. |
| 9. | Antiquarianism | Study of artifacts and old customs. |
| 10. | Apologia | Formal defense of beliefs or actions. |
| 11. | Archaeology | Study of past through material remains. |
| 12. | Archive | Repository of historical records. |
| 13. | Aristocracy | Rule by hereditary elite. |
| 14. | Armistice | Agreement to stop fighting temporarily. |
| 15. | Assimilation | Adoption of dominant culture by minorities. |
| 16. | Asylum | Protection granted to political refugees. |
| 17. | Autarky | Economic self-sufficiency policy. |
| 18. | Autobiography | Life story written by oneself. |
| 19. | Autocracy | Rule by a single unchecked leader. |
| 20. | Balance of power | Stability via countervailing state strength. |
| 21. | Balkanization | Fragmentation into smaller hostile units. |
| 22. | Bastion | Stronghold of power or defense. |
| 23. | Bicameralism | Legislature with two chambers. |
| 24. | Bill of Rights | Guaranteed legal and civil liberties. |
| 25. | Biography | Life story written by another. |
| 26. | Black Death | Fourteenth-century pandemic plague in Eurasia. |
| 27. | Blockade | Cutting off enemy supplies or access. |
| 28. | Bourgeoisie | Middle class owning capital. |
| 29. | Bureaucracy | Administrative system of officials and rules. |
| 30. | Caliphate | Islamic polity led by a caliph. |
| 31. | Capitalism | Private ownership and market exchange system. |
| 32. | Causation | Explanation of why events occurred. |
| 33. | Census | Official population count and data. |
| 34. | Centralization | Concentration of authority in a center. |
| 35. | Charter | Document granting rights or authority. |
| 36. | Chronicler | Writer compiling historical events. |
| 37. | Chronology | Arrangement of events by time. |
| 38. | Civil society | Nonstate associations shaping public life. |
| 39. | Civil war | Internal war within a state. |
| 40. | Clause | Distinct provision in a legal text. |
| 41. | Cold War | US–Soviet global rivalry without direct war. |
| 42. | Collective memory | Shared public recollection of the past. |
| 43. | Colonialism | Control of territories by foreign powers. |
| 44. | Commodification | Turning goods, labor, or ideas into commodities. |
| 45. | Common law | Judge-made law based on precedent. |
| 46. | Communism | Classless society via collective ownership ideal. |
| 47. | Comparative history | Cross-society analysis of similarities and differences. |
| 48. | Concordat | Agreement between state and church. |
| 49. | Conscription | Compulsory military service. |
| 50. | Constitution | Foundational framework of governance and rights. |
| 51. | Continuity | Persistence of structures over time. |
| 52. | Counterfactual | What-if scenario to test explanations. |
| 53. | Coup d’etat | Sudden illegal seizure of power. |
| 54. | Credibility | Trustworthiness of a source or claim. |
| 55. | Crusades | Medieval religious wars from Latin Christendom. |
| 56. | Cultural diffusion | Spread of cultural traits across groups. |
| 57. | Cultural history | Study of meanings, symbols, and practices. |
| 58. | Decolonization | End of imperial rule and independence. |
| 59. | Decree | Official order with legal force. |
| 60. | Demography | Statistical study of populations. |
| 61. | Dependency theory | Development shaped by unequal global relations. |
| 62. | Despotism | Tyrannical rule with absolute power. |
| 63. | Detente | Easing of international tensions. |
| 64. | Dialectic | Change through conflict of opposing forces. |
| 65. | Diaspora | Dispersed population maintaining homeland ties. |
| 66. | Diplomacy | Managing relations between states. |
| 67. | Divine right | Monarch’s authority claimed from God. |
| 68. | Domesday Book | 1086 English survey of landholding. |
| 69. | Dynasty | Ruling family line over generations. |
| 70. | Edict | Public proclamation by authority. |
| 71. | Empire | Multiethnic state ruling vast territories. |
| 72. | Enclosure | Privatization of common lands in Britain. |
| 73. | Enlightenment | Eighteenth-century emphasis on reason and rights. |
| 74. | Entente | Informal diplomatic understanding between states. |
| 75. | Epidemic | Rapid disease spread in a community. |
| 76. | Ethnogenesis | Formation of a new ethnic identity. |
| 77. | Ethnohistory | History using cultural and oral evidence. |
| 78. | Exile | Forced or voluntary banishment from homeland. |
| 79. | Fascism | Ultranationalist authoritarian mass politics. |
| 80. | Feudalism | Land-for-service hierarchy in medieval Europe. |
| 81. | Fiscal-military state | State built around taxation and war. |
| 82. | Footnote | Citation note supporting a statement. |
| 83. | Foreword | Introductory text by someone other than author. |
| 84. | Forgery | Faked document presented as authentic. |
| 85. | Frontier | Border zone of expansion or contact. |
| 86. | Gender history | Study of gender roles and power. |
| 87. | Genealogy | Study of family lineage. |
| 88. | Genocide | Intentional destruction of a people. |
| 89. | Geopolitics | Power shaped by geography and resources. |
| 90. | Glorious Revolution | 1688 English regime change and settlement. |
| 91. | Great Depression | Global economic collapse from 1929. |
| 92. | Hagiography | Idealized biography of a saint. |
| 93. | Hegemony | Dominance through consent and power. |
| 94. | Heritage | Valued legacy from the past. |
| 95. | Hermeneutics | Theory of interpreting texts and meanings. |
| 96. | Historiography | Study of how history is written. |
| 97. | Holocaust | Nazi genocide of Jews and others. |
| 98. | Humanism | Renaissance focus on classical learning and dignity. |
| 99. | Ideology | System of political or social ideas. |
| 100. | Imperialism | Expansion of power through domination abroad. |