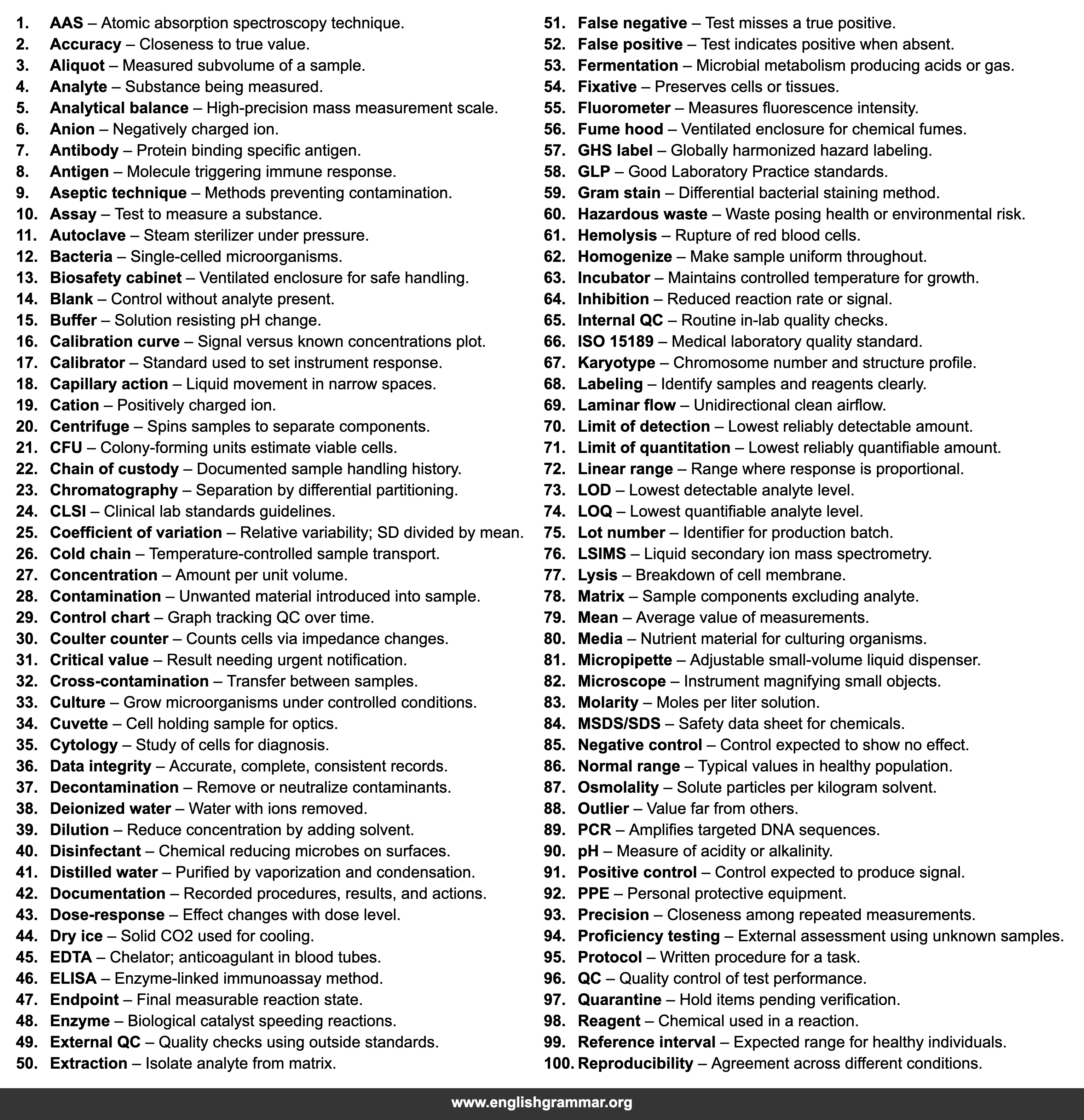
| No. | Term | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | AAS | Atomic absorption spectroscopy technique. |
| 2. | Accuracy | Closeness to true value. |
| 3. | Aliquot | Measured subvolume of a sample. |
| 4. | Analyte | Substance being measured. |
| 5. | Analytical balance | High-precision mass measurement scale. |
| 6. | Anion | Negatively charged ion. |
| 7. | Antibody | Protein binding specific antigen. |
| 8. | Antigen | Molecule triggering immune response. |
| 9. | Aseptic technique | Methods preventing contamination. |
| 10. | Assay | Test to measure a substance. |
| 11. | Autoclave | Steam sterilizer under pressure. |
| 12. | Bacteria | Single-celled microorganisms. |
| 13. | Biosafety cabinet | Ventilated enclosure for safe handling. |
| 14. | Blank | Control without analyte present. |
| 15. | Buffer | Solution resisting pH change. |
| 16. | Calibration curve | Signal versus known concentrations plot. |
| 17. | Calibrator | Standard used to set instrument response. |
| 18. | Capillary action | Liquid movement in narrow spaces. |
| 19. | Cation | Positively charged ion. |
| 20. | Centrifuge | Spins samples to separate components. |
| 21. | CFU | Colony-forming units estimate viable cells. |
| 22. | Chain of custody | Documented sample handling history. |
| 23. | Chromatography | Separation by differential partitioning. |
| 24. | CLSI | Clinical lab standards guidelines. |
| 25. | Coefficient of variation | Relative variability; SD divided by mean. |
| 26. | Cold chain | Temperature-controlled sample transport. |
| 27. | Concentration | Amount per unit volume. |
| 28. | Contamination | Unwanted material introduced into sample. |
| 29. | Control chart | Graph tracking QC over time. |
| 30. | Coulter counter | Counts cells via impedance changes. |
| 31. | Critical value | Result needing urgent notification. |
| 32. | Cross-contamination | Transfer between samples. |
| 33. | Culture | Grow microorganisms under controlled conditions. |
| 34. | Cuvette | Cell holding sample for optics. |
| 35. | Cytology | Study of cells for diagnosis. |
| 36. | Data integrity | Accurate, complete, consistent records. |
| 37. | Decontamination | Remove or neutralize contaminants. |
| 38. | Deionized water | Water with ions removed. |
| 39. | Dilution | Reduce concentration by adding solvent. |
| 40. | Disinfectant | Chemical reducing microbes on surfaces. |
| 41. | Distilled water | Purified by vaporization and condensation. |
| 42. | Documentation | Recorded procedures, results, and actions. |
| 43. | Dose-response | Effect changes with dose level. |
| 44. | Dry ice | Solid CO2 used for cooling. |
| 45. | EDTA | Chelator; anticoagulant in blood tubes. |
| 46. | ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunoassay method. |
| 47. | Endpoint | Final measurable reaction state. |
| 48. | Enzyme | Biological catalyst speeding reactions. |
| 49. | External QC | Quality checks using outside standards. |
| 50. | Extraction | Isolate analyte from matrix. |
| 51. | False negative | Test misses a true positive. |
| 52. | False positive | Test indicates positive when absent. |
| 53. | Fermentation | Microbial metabolism producing acids or gas. |
| 54. | Fixative | Preserves cells or tissues. |
| 55. | Fluorometer | Measures fluorescence intensity. |
| 56. | Fume hood | Ventilated enclosure for chemical fumes. |
| 57. | GHS label | Globally harmonized hazard labeling. |
| 58. | GLP | Good Laboratory Practice standards. |
| 59. | Gram stain | Differential bacterial staining method. |
| 60. | Hazardous waste | Waste posing health or environmental risk. |
| 61. | Hemolysis | Rupture of red blood cells. |
| 62. | Homogenize | Make sample uniform throughout. |
| 63. | Incubator | Maintains controlled temperature for growth. |
| 64. | Inhibition | Reduced reaction rate or signal. |
| 65. | Internal QC | Routine in-lab quality checks. |
| 66. | ISO 15189 | Medical laboratory quality standard. |
| 67. | Karyotype | Chromosome number and structure profile. |
| 68. | Labeling | Identify samples and reagents clearly. |
| 69. | Laminar flow | Unidirectional clean airflow. |
| 70. | Limit of detection | Lowest reliably detectable amount. |
| 71. | Limit of quantitation | Lowest reliably quantifiable amount. |
| 72. | Linear range | Range where response is proportional. |
| 73. | LOD | Lowest detectable analyte level. |
| 74. | LOQ | Lowest quantifiable analyte level. |
| 75. | Lot number | Identifier for production batch. |
| 76. | LSIMS | Liquid secondary ion mass spectrometry. |
| 77. | Lysis | Breakdown of cell membrane. |
| 78. | Matrix | Sample components excluding analyte. |
| 79. | Mean | Average value of measurements. |
| 80. | Media | Nutrient material for culturing organisms. |
| 81. | Micropipette | Adjustable small-volume liquid dispenser. |
| 82. | Microscope | Instrument magnifying small objects. |
| 83. | Molarity | Moles per liter solution. |
| 84. | MSDS/SDS | Safety data sheet for chemicals. |
| 85. | Negative control | Control expected to show no effect. |
| 86. | Normal range | Typical values in healthy population. |
| 87. | Osmolality | Solute particles per kilogram solvent. |
| 88. | Outlier | Value far from others. |
| 89. | PCR | Amplifies targeted DNA sequences. |
| 90. | pH | Measure of acidity or alkalinity. |
| 91. | Positive control | Control expected to produce signal. |
| 92. | PPE | Personal protective equipment. |
| 93. | Precision | Closeness among repeated measurements. |
| 94. | Proficiency testing | External assessment using unknown samples. |
| 95. | Protocol | Written procedure for a task. |
| 96. | QC | Quality control of test performance. |
| 97. | Quarantine | Hold items pending verification. |
| 98. | Reagent | Chemical used in a reaction. |
| 99. | Reference interval | Expected range for healthy individuals. |
| 100. | Reproducibility | Agreement across different conditions. |