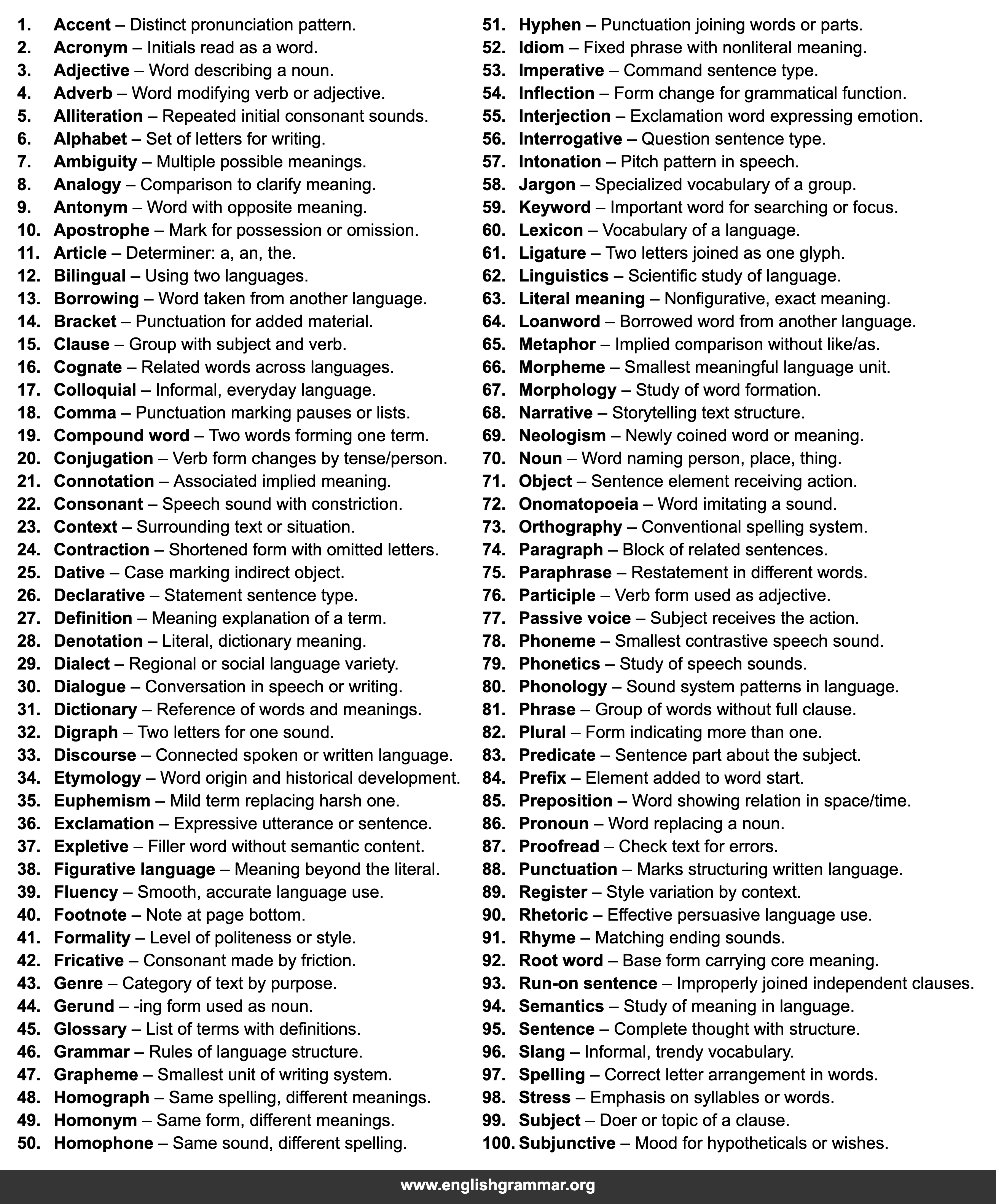
| No. | Term | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Accent | Distinct pronunciation pattern. |
| 2. | Acronym | Initials read as a word. |
| 3. | Adjective | Word describing a noun. |
| 4. | Adverb | Word modifying verb or adjective. |
| 5. | Alliteration | Repeated initial consonant sounds. |
| 6. | Alphabet | Set of letters for writing. |
| 7. | Ambiguity | Multiple possible meanings. |
| 8. | Analogy | Comparison to clarify meaning. |
| 9. | Antonym | Word with opposite meaning. |
| 10. | Apostrophe | Mark for possession or omission. |
| 11. | Article | Determiner: a, an, the. |
| 12. | Bilingual | Using two languages. |
| 13. | Borrowing | Word taken from another language. |
| 14. | Bracket | Punctuation for added material. |
| 15. | Clause | Group with subject and verb. |
| 16. | Cognate | Related words across languages. |
| 17. | Colloquial | Informal, everyday language. |
| 18. | Comma | Punctuation marking pauses or lists. |
| 19. | Compound word | Two words forming one term. |
| 20. | Conjugation | Verb form changes by tense/person. |
| 21. | Connotation | Associated implied meaning. |
| 22. | Consonant | Speech sound with constriction. |
| 23. | Context | Surrounding text or situation. |
| 24. | Contraction | Shortened form with omitted letters. |
| 25. | Dative | Case marking indirect object. |
| 26. | Declarative | Statement sentence type. |
| 27. | Definition | Meaning explanation of a term. |
| 28. | Denotation | Literal, dictionary meaning. |
| 29. | Dialect | Regional or social language variety. |
| 30. | Dialogue | Conversation in speech or writing. |
| 31. | Dictionary | Reference of words and meanings. |
| 32. | Digraph | Two letters for one sound. |
| 33. | Discourse | Connected spoken or written language. |
| 34. | Etymology | Word origin and historical development. |
| 35. | Euphemism | Mild term replacing harsh one. |
| 36. | Exclamation | Expressive utterance or sentence. |
| 37. | Expletive | Filler word without semantic content. |
| 38. | Figurative language | Meaning beyond the literal. |
| 39. | Fluency | Smooth, accurate language use. |
| 40. | Footnote | Note at page bottom. |
| 41. | Formality | Level of politeness or style. |
| 42. | Fricative | Consonant made by friction. |
| 43. | Genre | Category of text by purpose. |
| 44. | Gerund | -ing form used as noun. |
| 45. | Glossary | List of terms with definitions. |
| 46. | Grammar | Rules of language structure. |
| 47. | Grapheme | Smallest unit of writing system. |
| 48. | Homograph | Same spelling, different meanings. |
| 49. | Homonym | Same form, different meanings. |
| 50. | Homophone | Same sound, different spelling. |
| 51. | Hyphen | Punctuation joining words or parts. |
| 52. | Idiom | Fixed phrase with nonliteral meaning. |
| 53. | Imperative | Command sentence type. |
| 54. | Inflection | Form change for grammatical function. |
| 55. | Interjection | Exclamation word expressing emotion. |
| 56. | Interrogative | Question sentence type. |
| 57. | Intonation | Pitch pattern in speech. |
| 58. | Jargon | Specialized vocabulary of a group. |
| 59. | Keyword | Important word for searching or focus. |
| 60. | Lexicon | Vocabulary of a language. |
| 61. | Ligature | Two letters joined as one glyph. |
| 62. | Linguistics | Scientific study of language. |
| 63. | Literal meaning | Nonfigurative, exact meaning. |
| 64. | Loanword | Borrowed word from another language. |
| 65. | Metaphor | Implied comparison without like/as. |
| 66. | Morpheme | Smallest meaningful language unit. |
| 67. | Morphology | Study of word formation. |
| 68. | Narrative | Storytelling text structure. |
| 69. | Neologism | Newly coined word or meaning. |
| 70. | Noun | Word naming person, place, thing. |
| 71. | Object | Sentence element receiving action. |
| 72. | Onomatopoeia | Word imitating a sound. |
| 73. | Orthography | Conventional spelling system. |
| 74. | Paragraph | Block of related sentences. |
| 75. | Paraphrase | Restatement in different words. |
| 76. | Participle | Verb form used as adjective. |
| 77. | Passive voice | Subject receives the action. |
| 78. | Phoneme | Smallest contrastive speech sound. |
| 79. | Phonetics | Study of speech sounds. |
| 80. | Phonology | Sound system patterns in language. |
| 81. | Phrase | Group of words without full clause. |
| 82. | Plural | Form indicating more than one. |
| 83. | Predicate | Sentence part about the subject. |
| 84. | Prefix | Element added to word start. |
| 85. | Preposition | Word showing relation in space/time. |
| 86. | Pronoun | Word replacing a noun. |
| 87. | Proofread | Check text for errors. |
| 88. | Punctuation | Marks structuring written language. |
| 89. | Register | Style variation by context. |
| 90. | Rhetoric | Effective persuasive language use. |
| 91. | Rhyme | Matching ending sounds. |
| 92. | Root word | Base form carrying core meaning. |
| 93. | Run-on sentence | Improperly joined independent clauses. |
| 94. | Semantics | Study of meaning in language. |
| 95. | Sentence | Complete thought with structure. |
| 96. | Slang | Informal, trendy vocabulary. |
| 97. | Spelling | Correct letter arrangement in words. |
| 98. | Stress | Emphasis on syllables or words. |
| 99. | Subject | Doer or topic of a clause. |
| 100. | Subjunctive | Mood for hypotheticals or wishes. |